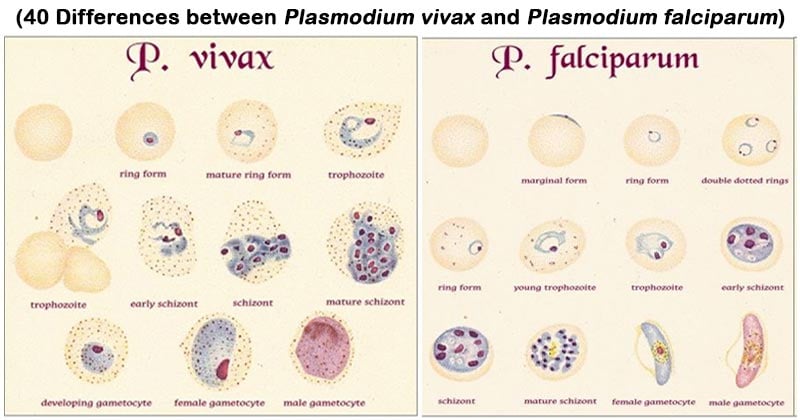
| S.N. |
Character |
Plasmodium vivax |
Plasmodium falciparum |
| 1. |
Disease Caused |
Benign tertian malaria |
Malignant tertian malaria |
| 2. |
Geographic area |
Tropics, Africa (rare in West Africa), Middle East, Asia, Central and South America. It is the most common geographically widespread species of Plasmodium causing malaria in human beings. |
Predominant species, worldwide tropics, but especially sub-Saharan Africa. |
| 3. |
Type of RBC invaded |
Primarily invades reticulocytes, young red cells. |
Invades all red cells regardless of age. |
| 4. |
Parasitized red cells |
Enlarged, pale. Fine stippling (Schüffner dots). |
Not enlarged. Coarse stippling (Maurer’s clefts). |
| 5. |
Color of cytoplasm ( in Giemsa stained thin blood smear) |
Decolorized, pale. |
Normal, bluish tinge at times. |
| 6. |
Level of usual maximum parasitemia |
Up to 30,000/μL of blood |
May exceed 200,000/μL;
commonly 50,000/μL
|
| 7. |
No. of merozoites released per infected hepatocyte |
30,000 |
10,000 |
| 8. |
Ring stage
trophozoites
|
Large rings (1/3–1/2 red cell diameter). Usually one chromatin granule; ring delicate. |
Small rings (1/5 red cell diameter). Often two granules; multiple infections common; ring delicate, may adhere to red cells. |
| 9. |
Pigment in developing trophozoites |
Fine; light brown; scattered |
Coarse; black; few clumps |
| 10. |
Late Trophozoite |
Medium Sized
Rarely amoeboid
Vacuole inconspicuous. |
Large
Markedly amoeboid
Vacuole prominent.
|
| 11. |
Late trophozoite shape |
Very pleomorphic |
Compact and rounded |
| 12. |
Schizont |
Small, compact,
Single pigmented mass
Seldom seen in the peripheral blood smear
|
Large, amoeboid,
Pigments coarse
Can be seen in the blood smear
|
| 13. |
Mature schizonts (segmenters) |
More than 12 merozoites (14–24) |
Usually more than 12 merozoites (8–32). Very rare in peripheral blood. |
| 14. |
Gametocytes |
Round or oval |
Crescentic |
| 15. |
Microgametocytes |
Kidney-shaped with blunt round ends.
Cytoplasm stains pale blue.Nucleus large.Chromatin diffuse.Granules fine, scattered.
|
Spherical, compact.
Cytoplasm stains pale light blue.Chromatin undivided.Granules abundant.
|
| 16. |
Macrogametocytes |
Crescentic.
Cytoplasm stains dark blue.Nucleus compact.Chromatin central.Pigment more compact.
|
Spherical.
Cytoplasm stains dark blue. Nucleus small.
Pigment diffuse ecoarse.
|
| 17. |
Distribution in peripheral blood |
All forms |
Only rings and crescents (gametocytes). |
| 18. |
Duration of asexual phase in man |
36-48 hrs
Usually 48 hrs
|
48 hrs |
| 19. |
Duration of sporogony in mosquito |
22-23 days at 20°C
10-12 days at 27°C
|
30 days at 17.5°C
10 days at 25-30°C
|
| 20. |
Duration of intrahepatic phase |
5.5 days |
8 days |
| 21. |
Duration of Schizogony |
12 days |
14 days |
| 22. |
Mechanism of Attachment and Receptor |
Merozoite (non–complement-mediated attachment), Duffy antigen |
Merozoite and glycophorin A and B |
| 23. |
Pigment Color |
Black and Dark Brown |
Yellow or Golden Brown |
| 24. |
Incubation period |
Incubation period (usually 10 to 17 days) |
Shortest of all the plasmodia, ranging from 7 to 10 days, and does not extend for months to years. |
| 25. |
Signs and Symptoms |
Patient experiences vague influenza-like symptoms with headache, muscle pains, photophobia, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. |
After the early influenza-like symptoms, P. falciparum rapidly produces daily (quotidian) chills and fever as well as severe nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The periodicity of the attacks then becomes tertian (36 to 48 hours), and fulminating disease develops. |
| 26. |
Symptom periodicity |
48 hr |
36-48 hr |
| 27. |
Complications |
Severe complications are uncommon in P. vivax infections, although coma and sudden death or other symptoms of cerebral involvement have been reported. |
Cerebral malaria, renal failure, circulatory collapse, severe anemia, hemoglobinuria, abnormal bleeding, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and jaundice. Acute cerebral malaria involves changes in mental status and if untreated may result in fatality within 3 days. |
| 28. |
Anemia |
Mild to moderate |
Severe |
| 29. |
CNS involvement |
Rare |
Very common |
| 30. |
Nephrotic syndrome |
Possible |
Rare |
| 31. |
Disease features |
P. vivax causes paroxysms of fever and chills every 48 hours; a spectrum of severe, life threatening syndromes similar to that with P. falciparum may be seen; a liver stage may cause relapses and recrudescences. |
P. falciparum produces daily (quotidian) chills and fever with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea progressing to tertian (36 to 48 hours) periodicity with fulminating disease (malignant tertian); no persistent liver stage. |
| 32. |
Severity of infection |
Comparatively less severe infection. |
Considered the most pathogenic and “deadliest” of all Plasmodium parasites. |
| 33. |
Mortality and Morbidity |
Relatively Lower |
Higher |
| 34. |
Prevalence |
The most prevalent of the human plasmodia. |
Comparatively less prevalent. |
| 35. |
Diagnosis |
Thick and thin blood smears; ring stage in RBCs with Schüffner dots |
Thick and thin blood smears; banana-shaped gametocytes; double rings in RBCs |
| 36. |
Main diagnostic criteria |
Large pale red cell; trophozoite irregular; pigment usually present; Schüffner’s dots not always present; several phases of growth seen in one smear; gametocytes appear as early as third day. |
Development following ring stage takes place in blood vessels of internal organs; delicate ring forms and crescent shaped gametocytes are only forms normally seen in peripheral blood; gametocytes appear after 7-10 days. |
| 37. |
Treatment |
Chloroquine (where no resistance), otherwise mefloquine or atovaquone/ proguanil, either followed by primaquine for relapse. |
Chloroquine (where no resistance); quinine sulfate plus doxycycline or plus tetracycline or plus clindamycin; atovaquone/ proguanil, mefloquine, bartesunate plus doxycycline or clindamycin; artemether/ lumefantrine (coartem). |
| 38. |
Duration of untreated infection |
5-7 years |
6-17 months |
| 39. |
Relapse |
Can relapse due to hypnozoites in liver |
No relapse |
| 40. |
Summarized distinguishing characteristics |
1. 48-hour cycle
2. Tends to infect young cells3. Enlarged RBCs4. Schüffner’s dots (true stippling) after 8-10 hours5. Delicate ring6. Very ameboid trophozoite7. Mature schizont contains 12-24 merozoites
|
1. 36-48-hour cycle
2. Tends to infect any cell regardless of age, thus very heavy infection may result3. All sizes of RBCs4. No Schüffner’s dots (Maurer’s dots: may be larger, single dots, bluish)5. Multiple rings/cell (only young rings, gametocytes, and occasional mature schizonts are seen in peripheral blood)6. Delicate rings, may have two dots of chromatin/ring, appliqué or accolé forms7. Crescent-shaped gametocytes
|